The sourcing of beet sugar vs cane sugar affects eco-friendliness in the sugar industry.
The sourcing of beet sugar vs cane sugar affects eco-friendliness in the sugar industry.
Blog Article
Discover the Uses and Perks of Beet Sugar Vs Cane Sugar in Your Daily Diet
Checking out the distinct top qualities of beet and cane sugar reveals even more than just their sweetening capacities; it highlights their unique effect on health and cooking arts. Beet sugar, understood for its refined flavor, is usually favored in delicate treats, whereas cane sugar, with its hint of molasses, includes splendor to robust meals. Each kind holds its own dietary account and glycemic ramifications, welcoming a deeper understanding of their functions in a well balanced diet and lasting intake practices.
Beginning and Manufacturing Procedures of Beet and Cane Sugar
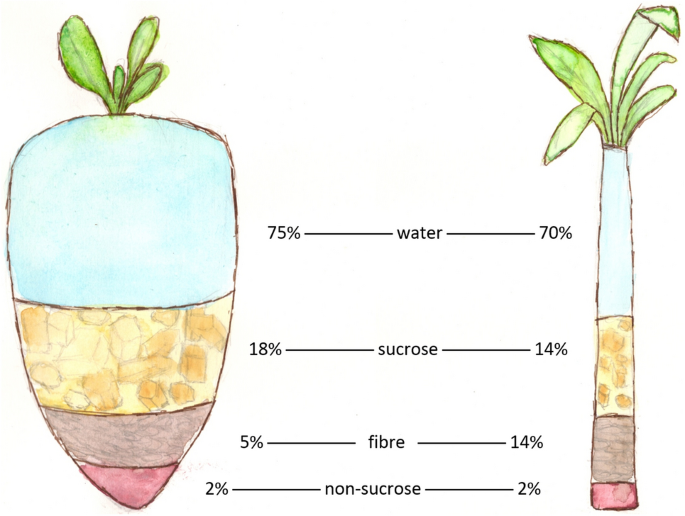
The distinct climates and dirt kinds required for growing sugar beetroots and sugarcane add to differences in their farming practices and geographical circulation, affecting the economics and sustainability of their manufacturing. beet sugar vs cane sugar.
Nutritional Contrast In Between Beet Sugar and Cane Sugar
In spite of stemming from various plants, beet sugar and cane sugar are nutritionally really comparable, both mainly including sucrose. Each supplies concerning 4 calories per gram, translating to approximately 16 calories per tsp. Structurally, both sugars are made up of approximately 99.95% sucrose, with minimal amounts of other compounds like wetness and trace minerals, which do not substantially modify their nutritional profiles.

Eventually, when selecting in between beet sugar and cane sugar based on nutritional site web material alone, both deal the same advantages and downsides as they are essentially forms of the same molecule-- sucrose, offering quick power without other nutrients.
Effect On Health: Glycemic Index and Caloric Content
Discovering even more into the results of beet sugar and cane sugar on health and wellness, it is essential to i thought about this consider their glycemic index and caloric web content. The glycemic index (GI) of both beet and cane sugar is around 65, categorizing them as high-GI foods, which can create quick spikes in blood sugar levels.
Each sort of sugar consists of about 4 calories per gram, making their calorie material matching. For those checking caloric consumption, particularly when managing weight or metabolic wellness conditions, recognizing this equivalence is important (beet sugar vs cane sugar). Extreme intake of any high-calorie, high-GI food can add to health problems such as excessive weight, heart illness, and insulin resistance.
Environmental and Economic Considerations of Sugar Manufacturing
Beyond health and wellness influences, the production of beet and cane sugar likewise elevates significant environmental and financial problems. Sugar beet growing has a tendency to call for cooler environments and has a lower geographical footprint contrasted to sugar cane, which flourishes in exotic areas. Both plants are extensive in terms of water usage and land occupation, potentially leading to logging and water scarcity. Financially, the international sugar market is highly volatile, influenced by modifications in worldwide profession plans and aids. Many nations incentivize sugar manufacturing via financial support, skewing market costs and impacting small farmers negatively.
In addition, using chemicals and plant foods in both beet and cane sugar growing can cause soil destruction and air pollution, more influencing biodiversity and regional water bodies (beet sugar vs cane sugar). The option between cultivating sugar beet or cane typically hinges on local environmental conditions and economic variables, making the sustainability of like it sugar manufacturing an intricate problem
Culinary Applications and Flavor Differences
While the environmental and financial elements of sugar manufacturing are undoubtedly significant, the selection between beet and cane sugar also affects culinary applications and taste accounts. Beet sugar, obtained from the sugar beet plant, is known for its extremely neutral taste.
Walking cane sugar, drawn out from sugarcane, often preserves molasses traces, which pass on a distinct splendor and depth. This mild molasses flavor boosts the complexity of baked items, sauces, and marinades. It is specifically favored in products where a sugar touch is desired, such as in brownies or gingerbread. Furthermore, the minor variant in wetness web content between beet and cane sugar can impact the appearance and consistency of recipes, making cane sugar a preferred selection for particular dishes that gain from its distinct residential or commercial properties.

Conclusion
Finally, both beet and cane sugar have distinct origins and manufacturing procedures, offering similar nutritional profiles with slight differences in salt web content and taste. While their influence on health and wellness, especially relating to glycemic index and calories, is comparable, the choice between them often steams down to ecological, economic elements, and specific cooking requirements. Comprehending these elements can direct consumers in making educated decisions that align with their wellness objectives and flavor choices.
Report this page